
Volume 22 Issue 2
May 18, 2021
ISSN 1099-839X
Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset: A Review of Cognitive
Flexibility and Its Implications for Dual-Language Education
Kandice S. Grote
California State University Northridge
Emily E. Russell
California State University Northridge
Olivia Bates
California State University Northridge
Rosemary Gonzalez
California State University Northridge
Abstract: The United States has seen an increase in cultural and linguistic diversity of student
populations. Policy makers have looked toward existing research in dual language education,
alternative curriculum, and bilingualism to support the needs of dual-language learners. In this
paper, we review two areas of research that have implications for educational policy, and also have
theoretical implications for early cognitive development. The first area focuses on cognitive
flexibility in bilingual populations. The second area focuses on growth mindset. We highlight the
parallels in these constructs, arguing that bilinguals may be uniquely receptive to growth mindset
interventions due to their increased cognitive flexibility. We identify specific ways that growth
mindset interventions could be applied to support dual-language learners. Lastly, we argue that
future research in both areas may provide researchers and educators with a better understanding of
early cognitive development in bilingual populations and the emergence of growth mindset in all
populations.
Keywords: Dual Language Learners; Bilingual Advantage; Growth Mindset, Multilingual
Education Policy; Cognitive Flexibility
Citation: Grote, K. S., Russell, E. E., Bates, O., & Gonzalez, R. (2021). Bilingual cognition and
growth mindset: A review of cognitive flexibility and its implications for dual-language education.
Current Issues in Education, 22(2). http://cie.asu.edu/ojs/index.php/cieatasu/article/view/1958
Accepted: 3/19/2021
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
1

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
Introduction
Over the past decade, the number of dual-language learners (DLLs) in the United States
has grown by 24% (Park et al., 2017). DLLs are defined as children 8 years and younger with at
least one parent who speaks a language other than English at home. This population now makes
up nearly one-third of all young children in the nation and more than 20% of the early childhood
population in 24 states (Park et al., 2017). The DLL population is a subset of English-language
learners (ELLs). ELLs are defined as students who are learning to speak English. They now
represent approximately 1 in 10 students in public schools (Sanchez, 2017). Despite these large
numbers, ELLs and DLLs are less likely than their peers to enroll in high-quality early childhood
education programs, which may delay readiness for kindergarten (Park et al., 2017). Without
native-language support, students may continue to exhibit academic lags through elementary
school and increased school dropout rates (McFarland et al., 2018). These realities have fueled a
movement towards supporting dual-language education and increasing its effectiveness.
Policy makers are currently looking to research for guidance on developing effective
instructional approaches for diverse classrooms (Sugarman & Geary, 2018). States like
California have passed legislation increasing the number of elementary dual-language education
programs (e.g., the 2016 Multilingual Education Act and the Global 2030 Initiative), but the
transition will take time and effort (e.g., bilingual teacher training, curriculum changes, etc.).
There are two promising areas of cognitive development research that may help policy makers
and educators identify successful practices in the classroom. The first area of research focuses on
the cognitive flexibility exhibited by bilinguals. Many studies suggest that proficiency in two (or
more) languages leads to enhanced executive function (EF) and metacognitive abilities, which in
turn leads to enhanced problem solving (Wiseheart et al., 2016) and memory abilities (Kroll et
al., 2012). By understanding the impact of bilingualism on children’s cognition, educators can
create more specialized approaches for instructing DLLs. The second area of research that may
help identify successful practices in the classroom is the study of growth mindset (GM), which is
the belief that one’s intelligence can improve. Research suggests that GM may be especially
valuable in helping students overcome academic challenges (Dweck, 2000). Indeed, a number of
elementary schools have recently incorporated GM training into their curricula (Claro & Loeb,
2017). GM training may promote DLLs’ academic persistence and success; however, research is
scarce.
In this review, we posit that bilingual students, including DL and/or EL, may be uniquely
receptive to GM interventions because they possess enhanced cognitive flexibility. Further, we
suggest that the integration of research on GM and the bilingual cognitive advantage has
important theoretical and practical implications. First, we will review current literature on the
bilingual cognitive advantage. Then, we will introduce a new conceptual model of GM,
highlighting parallels between proposed components of GM and the bilingual cognitive
advantage, and examine current methods of measuring GM. Lastly, we suggest possible GM
interventions for DL and EL students, and their parents and teachers.
The Bilingual Cognitive Advantage
Peal and Lambert (1962) were the first to document the "intellectual advantage” of
bilinguals. The authors compared monolingual French and bilingual French-English children on
a battery of cognitive tests and found that bilinguals outperformed monolingual peers, and
displayed enhanced mental flexibility. There is now a large body of research suggesting that,
compared to monolinguals, bilinguals possess enhanced attention (Soveri et al., 2011; Zhou &
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
2

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
Krott, 2016), EF (Blom et al., 2014; Brito et al., 2014), creativity (Kharkhurin, 2009, 2010),
metalinguistic awareness (Friesen & Bialystok, 2012), and memory (Brito et al., 2014; Schroeder
& Marian, 2012). These advantages are present throughout the lifespan (Bialystok et al., 2008).
Currently EF is considered both an example of cognitive flexibility and a potential
mechanism driving the bilingual cognitive advantage. Bilinguals are thought to develop
enhanced EF because they are managing their multiple languages all the time (Costa et al.,
2009). Several findings support the hypothesis that bilinguals’ languages are active
simultaneously (Kroll & Dussias 2013, Thierry & Wu 2007; Dijkstra, 2005) and that, in addition
to regulating their own language use, bilinguals need to attend to the language of the other
speaker, and choose the correct language in which to respond to, while suppressing the
interference of other languages. Thus, a bilingual speaker’s ability to construct explicit
representations of linguistic knowledge may result in an increased ability to control and process
information. This cognitive flexibility may lend itself to flexibility and advantages in GM.
Research on theory of mind, metacognition, EF, and attention support this possibility.
Another interesting finding regarding bilinguals is that theory of mind emerges earlier
among bilingual populations. Theory of mind is a form of perspective taking, specifically the
ability to ascribe mental states to others (Premack & Woodruff, 1978). For example, Kovács
(2009) found that more than twice as many 2- and 3-year-old Romanian-Hungarian bilingual
children passed a false-belief test than intelligence-matched 2 and 3-year-old Romanian
monolingual children. Several studies also provide evidence that bilingualism accelerates theory
of mind development (Diaz & Farrar, 2017; Farhadian et al., 2010; Goetz, 2003; Han & Lee,
2013); bilinguals’ enhanced theory of mind is correlated with higher EF (Bialystok & Senman,
2004; Goetz, 2003; Kovács, 2009). Studies suggest that the degree of EF is a significant
predictor of performance on theory of mind tasks (Devine & Huges, 2014), particularly those
involving attentional control. Enhanced attentional control could serve to regulate one’s own
mental state including their own beliefs and knowledge, while also directing attention to
someone else’s mental state (Devine & Huges, 2014; Schroeder, 2018). Theory of mind not only
involves the coordination of EF processes, but also reasoning, and conceptual skills (Carlson &
Moses, 2001; Carlson et al., 1998; Frye et al., 1995; Sabbagh et al., 2006; Wellman et al., 2001).
Taken together, this research suggests that young bilinguals possess enhanced attention,
metacognition, and cognitive flexibility before they enroll in elementary school. Importantly,
these are all proposed components of GM. Therefore, it is possible that the bilingual cognitive
advantage also includes GM. In other words, bilingual populations may possess increased
frequency of growth mindset and be especially receptive to GM interventions. However,
exploring this possibility further necessitates a careful examination of existing research on GM.
Growth Mindset and Cognitive Flexibility
Growth mindsets can be defined as implicit beliefs about the malleability of
intelligence—specifically how people perceive their own and others’ intelligence (Dweck, 2006).
Carol Dweck first introduced the idea of growth mindset (see Dweck & Leggett, 1988, for
review), and contrasted it with the idea of fixed mindset, the belief that intelligence is fixed and
unchanging (Dweck, 2000). A large body of work has identified multiple aspects of growth
mindset, including increased cognitive flexibility, metacognition (Rattan et al., 2018), motivation
and goal planning (Bostwick et al., 2017) and perceptions of ability and motivation (Schmidt et
al., 2017).
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
3
Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
A New Model of GM
Research on GM has spanned across multiple disciplines, including psychology and
education. Across studies, inconsistent operational definitions of GM have led to inconsistent
findings. Although some researchers and educators tout the positive outcomes associated with
having GM (e.g., Boaler, 2013; Yettick et al., 2016), others question the role of GM in increasing
cognitive flexibility—and even its validity as a construct (Bahník & Vranka, 2017; Dixson et al.,
2017; Orosz et al., 2017). To determine the validity of GM, and the usefulness of GM
interventions in educational settings, particularly those involving DLLs, the findings of GM
research must be systematically organized. To this end, we created a new conceptual model of
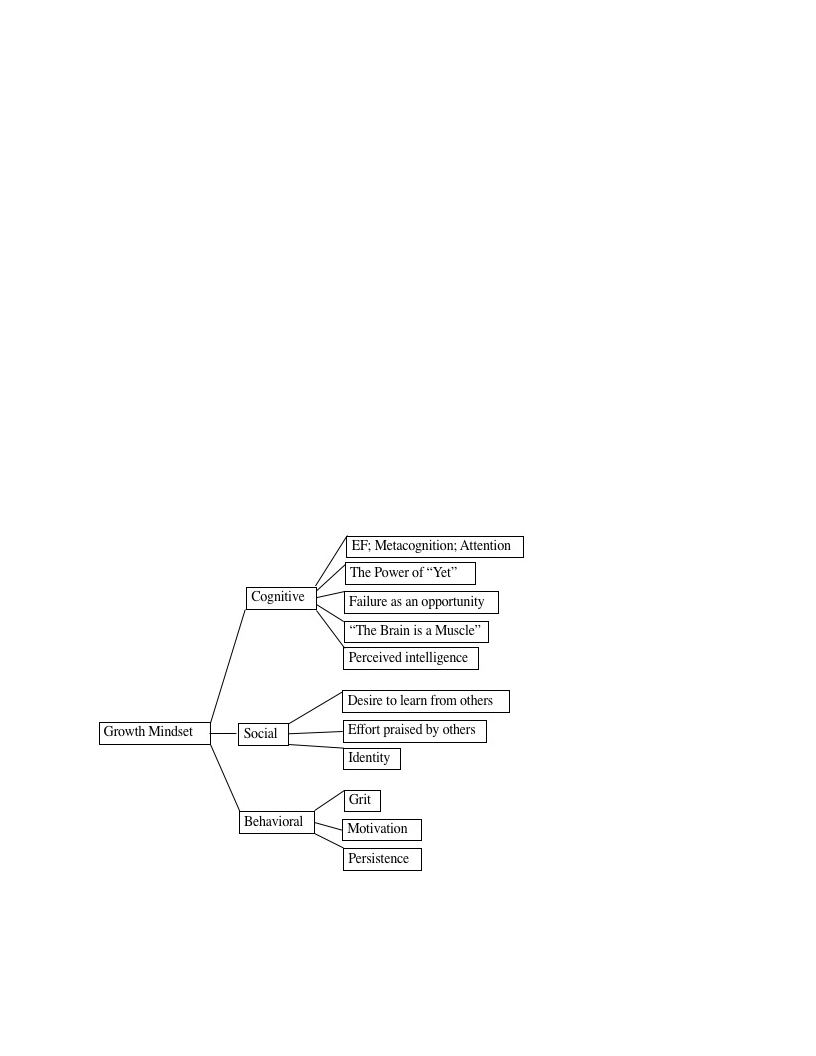
GM (see Figure 1).
Through a thorough review of the literature, we identified proposed components of GM
that have been supported by data. We then grouped these components into three domains:
cognitive, social, and behavioral. We believe this model provides more clear and comprehensive
answers to the questions, “What is GM?” and “How is GM nurtured within an individual?”. The
model also serves to highlights parallel between GM and the bilingual cognitive advantage. We
can identify a number of components of GM (e.g., metacognition, attention, and EF) that are also
abilities in which bilingual individuals excel. It is these commonalities that should be
investigated further, as they may carry important implications for academic interventions for EL
and DL populations. We elaborate on the model below.
Figure 1
Proposed Growth Mindset Model Components and Subcomponents
The cognitive domain encompasses components of GM having to do with an individual’s
mental functions and flexibility (Ravenscroft et al., 2012), specifically EF and attention
(Schroder et al., 2017) as well as perceptions of intelligence as malleable. Research has shown
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
4

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
that belief in the power of “yet” enhances individuals’ ability to apply effective learning
strategies in the face of academic and linguistic challenges (Blackwell et al., 2007). The power of
“yet” is a type of cognitive reframe and refers to a shift in thought that expands what is possible.
It is widely known in the field of cognitive behavioral therapy and the application of cognitive
restructuring that shifting one's thoughts can alter one's emotions and behaviors (e.g., Knapp &
Beck, 2008). This process can also apply to beliefs about one’s academic potential. Using the
words “not yet,” to contextualize a failure emphasizes to the students that the outcome is not
final (Dweck, 2006). Framing failure as temporary may inspire hope of future success and thus
increase students’ persistence. A concept that dovetails with the power of yet is the idea of “the
brain as a muscle,” which challenges the commonly-held naive theory that biology trumps
experience (Dweck, 2008). In other words, using the phrase “the brain is a muscle” can begin to
counter the cognitive schema that intelligence is fixed.
The social domain of GM encompasses the ways in which social partners or norms may
influence individual effort as well as the individuals’ identity in relation to others. It
encompasses effort praised by others, which emphasizes how external feedback can influence
our formation and maintenance of GM (Dweck, 2007). If only the outcome of effort is praised,
individuals may learn to value the outcome rather than the experience of learning. They may
seek tasks that prove their intelligence and avoid ones that do not (Dweck, 2006). They may even
hide their mistakes (Nussbaum & Dweck, 2007). In contrast, individuals who receive external
praise for the effort will be more likely to engage with and seek challenges and be less concerned
with how they appear or compare socially. Identity speaks to this outcome and the social
elements that influences our mindsets and our academic perception of ourselves as learners. For
example, the perception of failure as an opportunity could impact both a self- and social-identity
whereby individuals who view failure as an opportunity may seek to learn from others versus be
threatened by their success (Dweck, 2006).
The behavioral domain encompasses individuals’ actions that exemplify and/or sustain
GM. Persistence speaks to an individual’s ability to continue on a challenging task. This
component may also include increases in strategy use, overall motivation, and overall
performance (O’Rourke et al., 2014). We found a similar series of behavioral traits in the
component of grit (Duckworth et al., 2007). Like GM, grit is a multifaceted construct.
Duckworth et al. (2007) discuss grit as both passion and perseverance. Therefore, we suggest
that grit falls under both the social domain (e.g., passion and courage) of GM as well the
behavioral domain (e.g., perseverance and action) of GM.
Measuring the GM Framework
While each component in the proposed GM model has been investigated experimentally,
no studies have examined them in regard to DL and EL populations. In addition, studies on GM
have relied on brief, self-report questionnaires, which are limited in capturing cognitive
processes through a set of uniform tasks in an experimental design. In other words, self-report
questionnaires (a) make it difficult to identify specific areas and components of GM; and (b)
have limited validity/reliability among youth who are not yet literate or balanced bilinguals.
Recently, studies have begun to use more objective measures of GM, including neurological
paradigms (Moser et al., 2011; Schroder et al., 2017). For instance, Mangels, Butterfield, Lamb,
Good, and Dweck (2006) tested adults’ general knowledge on a variety of academic domains
(e.g., art and music history, world and US history, etc.) and measured brain activation via ERP in
addition to self-report questionnaires. The researchers found that the participants’ beliefs
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
5

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
influenced learning success through increased attention and conceptual processing and that
participants were more likely to correct their mistakes on a surprise retest (Mangels et al., 2006).
Moser, Schroder, Heeter, Moran, and Lee (2011) extended these initial findings by identifying
evidence of conscious attention allocation towards errors, and overall improved performance
during a surprise retest. Both of these studies suggest a relationship between attention and GM.
Schroder, Fisher, Lin, Lo, Danovitch, and Moser (2017) replicated this previous correlational
work and found growth-minded children also demonstrated better accuracy after mistakes
(Mangels et al., 2006; Moser et al., 2011). These studies aimed to identify how beliefs influenced
attention on a moment-to-moment basis and provide support for a neurocognitive model of a
GM. The findings of these studies on the cognitive flexibility associated with GM may inform
our understanding of the cognitive flexibility associated with bilingualism. Cognitive flexibility
could speak directly to the EF cognitive flexibility. Investigating similarities between the
mechanisms underlying both GM and EF may help researchers identify more appropriate
measures for DL and EL populations.
The first author of this paper is pursuing two veins of research that investigate the
development of GM, and the effectiveness of GM interventions in younger populations. The first
aim is to assess GM in younger children who may struggle with language- or literacy-based
paradigms. Focusing on younger populations offers the opportunity to understand when GM
emerges and how GM interventions might be implemented. Thus far, only a few studies have
found that GM is present in kindergarten and first-grade populations (Cain & Dweck, 1995;
Smiley & Dweck, 1995). Understanding how and when GM develops among younger children
may be especially useful given that initial transitions from pre-K to formal educational settings
often have the most impact on academic achievement (Blackwell et al., 2007; Dweck et al.,
1995).
We have created a series of vignettes for use with 4- to 6-year-old children that we
believe improves on existing measures of GM in younger populations in a number of ways. First,
the vignettes are designed to be read aloud to children and are coupled with pictures to
circumnavigate any language or literacy barriers. Each vignette describes a problem with a
particular outcome (e.g., A child character is asked by the teacher to count to ten [problem] and
the child counts to 10 without making a mistake [outcome]). The problems themselves are
cognitive, social, and behavioral in nature—in other words, not limited to academic performance,
which is a realm in which children of this age are only just becoming exposed to. After being
read the vignette, children are asked to reason about the outcome; their attributions of the child
character’s successes and failures are classified as consistent with GM (e.g., the character’s
practice, hard work, increased effort) or fixed mindset (e.g., the character’s luck or natural
talent). This measure will help us determine when cognitive aspects of GM emerge for
monolingual and bilingual children. However, we hypothesize that, compared to monolingual
children, bilingual children will exhibit GM earlier and more frequently, due to their enhanced
theory of mind and EF.
The second area of our research seeks to identify the potential benefit of a GM
intervention to enhance persistence in completing a challenging problem-solving task. In this
study, 4- to 6-year-old children’s baseline GM is measured using the methodology described
above. Next, they are asked to participate in a challenging task, during which their degree of
persistence is measured. Children then participate in a GM intervention, followed by another
challenging task. Lastly, children’s GM is assessed. The intention is to compare pre-and-post
intervention persistence and GM scores. We predict that an intervention will increase both
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
6

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
persistence and GM scores, but that bilingual participants will demonstrate more flexibility in
their perceptions of intelligence and persist longer when challenged. This study builds upon
previous research by introducing a novel approach to testing the behavioral components of GM.
Both of these studies are in the early stages of piloting, but we are confident they will be integral
first steps towards enhancing our ability to assess GM among younger populations, especially
those who are bilingual, and improve methodological challenges in assessing GM.
Importantly, each of these studies are coupled with cognitive flexibility tasks commonly
assessed with bilingual populations to identify potential relationships between elements of GM
and bilingual cognition. However, given our review of EF, attentional control, cognitive
flexibility, and reasoning, we see potential for a bilingual GM advantage. We cannot claim that
bilingualism leads to GM, but we do suggest that learning more about the mechanisms of
cognitive flexibility in bilingual populations may tell us more about how increased cognitive
flexibility could benefit all children. Additionally, these studies may provide additional
information about how language impacts the brain and how children’s educational success can
be attributed to learning more than one language.
Implications for Dual Language Academic Achievement and Intervention
Although definitions of GM vary across studies, there is agreement that GM ideology has
implications for improving learning environments, class culture, and academic intervention
(Schmidt et al., 2017; Rattan et al., 2018). Likewise, many studies suggest that possessing a GM
can be advantageous in academic settings (e.g., Blackwell et at., 2007; Bostwick et al., 2017;
Schmidt et al., 2017). Conversely, possessing a fixed mindset can lead to lack of persistence
during moments of increased difficulty, and feelings of failure or defeat (Dweck & Leggett 1988;
Rattan et al., 2018; Reavis et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2019). For this reason, promoting GM in
students has become a popular academic intervention (Blackwell et al., 2007; Chao et al., 2017;
Dixson et al., 2017; Enriquez et al., 2017; Schmidt et al., 2017). However, only recently have
studies begun to investigate how students’ mindsets predict their learning or achievement (Claro
& Loeb, 2017).
Two studies have looked at this relationship on a larger scale (Claro & Loeb, 2017;
Yeager et al., 2019). Both studies identified the long-term economic and social impacts of GM in
diverse populations. The findings of Yeager et al. (2019) suggest that GM interventions need not
be within the classroom at all. Subjects participated in a short online GM intervention, which
taught them that intellectual abilities can be developed. Training resulted in improved grades
among 6,320 lower-achieving ninth grade students. These results are especially encouraging
because they suggest that GM interventions can be successfully implemented with minimal
funding, teacher training, and time taken away from the students’ other school-related tasks. A
recent report from the Brookings Institute assessed the responses to a GM measure from 125,000
students in third-eighth grade, across five school districts in California (Claro & Loeb, 2017).
This study found students with a stronger GM learn more in a given year compared to those with
lower GM. It also found that traditionally underserved students including students in poverty,
ELLs, and ethnic-minority students, are less likely to hold a GM (Claro & Loeb, 2017).
Although this study revealed that all groups with a GM learn more over the course of a year than
those who do not have a GM, further research is needed to identify how mindsets vary across
socioeconomic status, ethnicity, and are particularly important for at-risk populations (Claro &
Loeb, 2017).
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
7

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
Additionally, this area of research may reveal why at-risk populations are prone to low
levels of GM given factors such as perceptions of structural barriers of success (e.g., perceptions
of inequality in accessing opportunity, stereotype threat, etc.; Claro & Loeb, 2017). In the United
States, ELLs make up a large part of these at-risk populations, and DLL programs seem to have
offered some recourse for these programs, however it is clear that more is needed to close the
achievement gap. DL programs are one way to remedy these gaps.
Studies suggest that students enrolled in DL programs excel academically (Valentino &
Reardon, 2015) and emotionally (Lindholm-Leary & Borsato, 2001) and develop cross-cultural
competence (Lindsey et al., 2009). DL programs can also close the achievement gap for ELLs
(Collier & Thomas, 2012). One approach to addressing this gap is to identify the role of language
proficiency in cognitive development. We know that balanced bilinguals (i.e., those with
proficiency in both languages) demonstrate more success on challenging tasks and tasks that
have higher cognitive demand (Bialystok et al., 2005; Yoshida, 2008). Research suggests this is
due to the higher demand of switching between languages (Bialystok, 2017). By investigating
the relationship between language use and cognitive flexibility among bilingual populations,
researchers may be able to identify potential GM interventions for language learners. Together,
both EF (Best et al., 2011) and GM are significant predictors of academic performance and GM
may be likely to respond with enhanced resilience when challenged and show greater learning
and achievement in the face of difficulty (Dweck, 2006).
Since GM studies have been conducted at the elementary school level, we recommend
researchers examine the effectiveness of early GM interventions within educational settings
particularly during the initial transitions into formal schooling. These years can be challenging
for children and often predict later achievement and success within school settings (Duncan et
al., 2007). Educators and policy makers alike may become increasingly invested in examining
GM interventions to support high quality early childhood multilingual education. Therefore, now
may be an opportune time to conduct this research given the increasing need to support ELLs
(Park et al., 2018) and DLs (Department of Education, 2015). Incorporating alternative methods
to predict student success would require the development of evaluative measures of GM,
particularly for accountability and assessment (Goldhaber & Özek, 2019). Thus, multilingual
learning environments provide a rich context to explore these questions in order to optimize
language learning environments.
There is a clear need to better support native language development in the classroom.
Implementing GM interventions may address these concerns, and may inevitably be applicable
to all early education populations. There is still very little we know regarding what mindsets
children hold, at what age, how mindsets vary from grade-to-grade, the validity and reliability of
GM measures, and if whether GMs are significant predictors of academic learning. What we
know so far, does show promise of immediate practical application and the benefit of an
approach aimed towards helping all children become intrinsically motivated to learn.
Practical Implications
In this paper, we have highlighted GM in bilingual individuals as a promising area of
research, with important theoretical implications. We turn our attention now to some possible
benefits of using GM inventions in educational settings, especially those with EL and DL
populations.
EL and early DL populations face a unique challenge: They are often labeled as
“behind”—linguistically and academically—upon entering the classroom. Many ELLs and early
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
8

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
DLLs feel stigmatized and inferior compared to more proficient speakers (Banse & Palacios,
2017). Additionally, their lack of proficiency results in negative preconceptions of ability and
intelligence (Jones & Mixon, 2016), resulting in a lack of motivation for learning (Williams,
2014), which may result in more of a fixed mindset. For example, DLLs sometimes experience
initial vocabulary delays in one language, which may lead to initial lower academic performance
(Meisel, 2004; Paradis et al., 2011; Pearson et al., 1997). Additionally, DLLs often exhibit lower
scores in literacy in English due to their ongoing acquisition of two vocabularies (Williams,
2014).
While younger DLLs eventually catch up and exceed monolingual scores in later grades
(Scheffner Hammer et al., 2014), these initial dips may leave DLLs feeling inadequate, or behind
their peers (Williams, 2014) and therefore may leave DL programs prematurely (Ackerman &
Tazi, 2015). Efforts toward addressing the achievement gap for ELLs have often relied on
segregation from mainstream classrooms either in the form of (1) temporary instruction (e.g.,
ELLs are removed for additional instruction) or (2) separate dedicated classrooms (e.g., SEI
programs; Jones & Mixon, 2016). However, research suggests these efforts only exacerbate the
stigma of being an ELL (Jones & Mixon, 2016) and that separation within schools lead to
feelings of social isolation from the greater school community (Klingner et al., 1998). In
contrast, researchers suggest greater inclusivity of peers within the classroom, less division, and
more positive self-esteem when ELLs are enrolled in DL programs (Plazza et al., 2015).
Research found that when ELL students are instructed in both their primary language and
English, they achieve higher scores on tests of reading and math in English when compared to
ELLs in monolingual English-only settings (Genesee et al. 2006). However, DL programs are
not without their own challenges. DL programs face obstacles in identifying and implementing
effective approaches in the classroom to help students through early language dips and maintain
motivation for attaining dual language proficiency (Ackerman & Tazi, 2015). Some programs
have attempted to utilize vocabulary-building interventions, but findings suggest that they may
not be powerful enough to close the achievement gap (Marulis & Neuman, 2013).
In-class GM interventions for ELLs and DLLs may be a way to maximize the benefits of
DL programs, by reducing fixed mindsets and improving levels of positive beliefs and
approaches towards the learning process as a whole. The potential benefits of GM interventions
may also be applicable for both DLL educators and parents.
Developmentally Appropriate GM Pedagogy
One potential solution to address the challenges faced by ELLs and DLLs is to integrate
research-based GM pedagogy in the classroom. For example, Brainology is a 4-unit program (40
mins per unit) for children ages 10-14 that integrates GM components (e.g., the brain is a muscle,
praising effort to improve self-efficacy) and walks the learner through understanding how the
brain grows and learns over time (Mindset Works Inc., 2017). This concept presents learning as
something of a long-term ongoing learning marathon, rather than an immediate sprint. There is
some promising data suggesting the Brainology training can shift GM – at least in the short-term.
After the success of Brainology, another program was developed for younger children. Growing
Early Mindsets (GEM), released in 2019, adapts elements of the Brainology program for
children in PreK-3rd learning environments, integrating GM, socio-emotional learning, and
mindfulness principles and practices (Mindset Works Inc., 2017). The added element of socio-
emotional learning and mindfulness is especially applicable since younger children are beginning
to self-regulate their emotions and develop their sense of self at this time. More research is
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
9

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
needed to determine the long-term effects of these programs, but GM training with younger
children could be useful – especially so for ELLs and DLLs who face early language learning
challenges.
We suggest two critical features of a successful pedagogy: a) emphasizing different
components of GM at developmentally appropriate times; and b) providing long-term
scaffolding to promote long-term retention of ideas and change in mindset. Given that successful
DL programs begin early (Pre-K) and build momentum through high school, the implementation
of GM pedagogy should be ongoing and evolve to meet the unique demands required for dual
language acquisition. To accomplish this, we suggest introducing GM components that map onto
children’s natural developmental milestones. For example, some GM components may be more
salient to younger language learners than others.
In preschool or kindergarten, children who are beginning to recognize and control their
own feelings and emotions may be more adept at identifying and contextualizing challenges or
problems before they can develop GM strategies to overcome them. Educators can connect the
emotional component of learning to help foster children’s sense of agency and self-efficacy to
build a future framework for how to approach future problems or challenges (Enriquez et al.,
2017). This can be done by reading stories about characters experiencing challenges and creating
games around identifying those challenges. Once identified, educators can scaffold concepts of
resilience, optimism, and early goal setting, in addition to celebrating initial milestones (Lippard
et al., 2018). These components of GM are related to the process of learning and directly mirror
the process of emotional development among this age group (e.g., recognizing and managing
your emotions, planning responses, etc.).
As children develop, early GM pedagogy can begin to form schemas of neuroplasticity-
“the brain is a muscle.” The idea of the brain as a muscle might be particularly salient because it
is a concrete analogy that children can understand. Educators have also introduced the
idea/metaphor that problems and challenges are chances to “grow our brains,” and that this
experience can make people feel strong, happy, and excited to learn new things (Pawlina &
Stanford, 2011). Therefore, by engaging a child’s imagination through playful and relatable
images, GM interventions may also result in children becoming encouraged to make multiple
attempts at a hard task- tasks that they tackle because they are framed as “strengthening their
brains.” In later years, when children strive towards independence, a developmentally-
appropriate GM intervention may reinforce efforts towards self-efficacy.
The benefit of this intervention would be two-fold: a) different components of GM are
emphasized at developmentally appropriate times; and b) the spaced training would promote
long-term retention of ideas and change in mindset. These approaches are crucial for
multicultural environments that require more cognitively complex thinking to develop caring
about others who exhibit differences linguistically and culturally (Hanson et al., 2016). GM
curriculum also supports children’s ethno-racial socialization in a context where DL programs
value both languages. By growing in the ability to engage multiple perspectives and strategies
for solving problems may counter the myth of “one right way” of doing things (Enriquez et al.,
2017) and support greater concern for others who exhibit differences linguistically and culturally
(Hanson et al., 2016).
DLL educators’ professional development
DL educators experience ongoing, targeted professional development that ensures they
possess the expertise that is necessary for DLLs’ academic success (Ortiz & Fráquiz, 2017). DLL
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
10

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
educators are often overwhelmed by the limitations of bilingual programs, including but not
limited to, availability of classroom materials in both languages, everchanging policy changes,
and pressure to integrate research and pedagogy (Ackerman & Tazi, 2015). Unlike English-only
programs, few DL programs are housed in public schools and are often found within Charter and
independent schools (Christy et al., 2014; U.S. Department of Education, 2015). Coincidently,
DL educators, like their students, may also feel inadequate within the demands of these language
learning environments. Therefore, GM interventions may also have bidirectional benefits for
educators in regard to in-classroom practice, professional development and maintaining positive
morale.
DL educators must be up-to-date on policy recommendations, and newly available
resources for DL programs. Coincidently, DL educators, like their students, may also feel
inadequate within the demands of these language learning environments. Therefore, GM
interventions may also have bidirectional benefits for educators in regard to in-classroom
practice, professional development and maintaining positive morale.
Teacher efficacy matters, especially in implementing the interventions we have
described. To achieve much of what has been described thus far, educators must also possess
GM (Dweck & Leggett, 1988; Fraser, 2018). Studies suggest that teachers with lower teaching
efficacy are also less engaging with children (Lippard et al., 2018). This suggests that teachers
may need support as individuals to effectively engage children. If DL educators are fixed in
their own teaching methodology, they may not take advantage of opportunities to affirm and
validate DL linguistic resources and language learning experiences. Like their students, DL
educators may already be feeling ongoing pressure surrounding proficiency and testing and may
benefit from GM themselves when feeling overwhelmed. For this reason, we need educators
equipped with GM strategies and efficacy to take on the multiple challenges they face within
multilingual educational environments.
We suggest that GM interventions become an integrative part of the DL teacher-training
process so that educators may feel confident integrating GM into existing classroom pedagogy.
Like any K-12 teacher, each educator must possess the necessary foundation knowledge to teach
their students effectively. Therefore, educators also need to be well-versed in GM and its
components. This GM expertise may help DL educators take on the immediate and upcoming
challenges within DL education with a proactive approach that will help in decreasing negative
feelings toward the ongoing changes within multilingual education. The potential here is to
increase self-efficacy for the educator so that they can model GM for students in the classroom
and effectively encourage parents to support GM at home. Teachers can do this by showing
enthusiasm for learning new things and bring awareness to fellow teachers, students, and parents,
to the times when effort and practice yielded positive results.
DL Parents
Dual language learning is most effective when the support for learning two languages
continues at home (Lindholm-Leary, 2005). Several studies support parental involvement both at
the school and the home, and in some cases incorporate the community. Ideally, GM curriculum
would support both the child in the classroom and at home in developing biliteracy.
Parents of DLLs are often worried about the timing and trajectory of their children's
language acquisition. Parents are often dismayed by low test scores, and sometimes prematurely
remove their children from DL programs before their children have experienced their eventual
vocabulary gains (Jones & Mixon, 2016). For example, English-only parents who enroll their
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
11

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
kindergartener who is in a 90/10 model (where 10% is English instruction), may immediately be
concerned their child’s lack of English proficiency. In some circumstances, older EL parents
may be asked to share with younger parents to trust the process of language acquisition and share
their own experiences with early language lags (Ackerman & Tazi, 2015). Alternatively, staff
and educators may attempt to teach the parents about DL models and the process of biliteracy
development in this context. However, neither of these approaches may be sufficient to yield
long-term results.
DL schools are already overburdened and are often tasked with parental outreach and
recruitment. One way to ease this burden is to provide GM interventions for parents in an effort
to help them understand that language learning is an ongoing process. For example, if parents
were to experience a GM intervention, they would learn that the brain as a muscle and
incremental growth of intelligence is similar to their child’s linguistic experiences. Over time,
their vocabulary will grow, just like their brain. GM interventions may also assist parents of
early-grade DLLs that the arch of language proficiency takes time and feel encouraged to
contribute rather than doubt the DL process entirely. We would also recommend that these GM
interventions for parents integrate the families’ native language to help promote school-based
interventions and to help promote at-home support for children’s learning (Mendez &
Westerberg, 2012). One possibility is to provide take-home short stories as part of the school
curriculum that feature GM and fixed mindset scenarios for parents to read to their children.
These stories may be formatted similar to our current research. Through this method, parents can
support discussions of mindsets while simultaneously supporting their native language and
literacy development. By slowly integrating GM across each of these populations, we may help
ease the transition of dual language acquisition for all.
Conclusion
By proposing a new conceptual model of GM, we have identified promising areas of
research on both GM and the bilingual cognitive advantage. We have argued that studying GM
in younger and bilingual populations presents a unique and important opportunity to learn more
about how all children develop cognitive flexibility. We have proposed specific ways in which
DLLs, and their educators and parents, may benefit from GM interventions. However, prior to
significant investment in GM-oriented curricula, further research and improved methodology is
necessary. In sum, by understanding how GM emerges in early development and across
demographics, we may ensure that all children persist in their learning and thrive academically.
References
Ackerman, D. J., & Tazi, Z. (2015). Enhancing young Hispanic dual language learners’
achievement: Exploring strategies and addressing challenges. (Policy Information Report,
ETS Research Report No. RR-15-01). Educational Testing Service.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ets2.12045.
Bahník, Š., & Vranka, M. A. (2017). Growth mindset is not associated with scholastic aptitude in
a large sample of university applicants. Personality and Individual Differences, 117, 139-
143.
Banse, H. & Palacios, N. (2017). Supportive classrooms for Latino English language learners:
Grit, ELL status, and the classroom content. The Journal of Educational Research,
111(6), 645-656.
Best, J. R., Miller, P. H., & Naglieri, J. A. (2011). Relations between executive function and
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
12

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
academic achievement from ages 5 to 17 in a large, representative national sample.
Learning and Individual Differences, 21, 327-336.
Bialystok, E. (2017). The bilingual adaptation: How minds accommodate experience.
Psychological Bulletin, 143(3), 233-262.
Bialystok, E., Craik, F. I. M., & Luk, G. (2008). Cognitive control and lexical access in younger
and older bilinguals. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and
Cognition,34(4), 859-873.
Bialystok, E., Martin, M. M., & Viswanathan, M. (2005). Bilingualism across the lifespan: The
rise and fall of inhibitory control. International Journal of Bilingualism, 9, 103-119.
Bialystok, E., & Senman, L. (2004). Executive processes in appearance-reality tasks: The
role of inhibition of attention and symbolic representation. Child Development, 75,
562-579.
Blackwell, L., Trzesniewski, K., & Dweck, C. (2007). Implicit theories of intelligence predict
achievement across an adolescent transition: A longitudinal study and an intervention.
Child Development, 78, 246-263.
Blom, E., Küntay, A.C., Messer, M., Verhagen, J., & Leseman, P. (2014). The benefits of being
bilingual: Working memory in bilingual Turkish-Dutch children. Journal of
Experimental Child Psychology, 128, 105-119.
Boaler, J. (2013). Ability and mathematics: The mindset revolution that is reshaping education.
FORUM, 55(1), 143-152.
Bostwick, K. C. P., Collie, R. J., Martin, A. J., & Durksen, T. L. (2017). Students’ growth
mindsets, goals, and academic outcomes in mathematics. Zeitschrift für Psychologie,
225(2), 107–116.
Brito, N. H., Grenell, A., & Barr, R. (2014). Specificity of the bilingual advantage for memory:
Examining cued recall, generalization, and working memory in monolingual, bilingual,
and trilingual toddlers. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 1369.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01369
Cain, K. M., & Dweck, C. S. (1995). The relation between motivational patterns and
achievement cognitions through the elementary school years. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly,
41(1), 25–52.
Carlson, S., & Moses, L. J. (2001). Individual differences in inhibitory control and children’s
theory of mind. Child Development, 72, 1032-1053.
Carlson, S. M., Moses, L. J., & Hix, H. R. (1998). The role of inhibitory processes in young
children’s difficulties with deception and false belief. Child Development, 69, 672-691.
Chao, M. M., Visaria, S., Mukhopadhyay, A., & Dehejia, R. (2017). Do rewards reinforce the
growth mindset?: Joint effects of the growth mindset and incentive schemes in a field
intervention. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 146(10), 1402-1419.
Claro, S., & Loeb, S. (2017). New evidence that students’ beliefs about their brains drive
learning. Evidence Speaks Reports, 2(29), Retrieved
from https://www.brookings.edu/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/claro-and-loeb-report.pdf.
Collier, V. P., & Thomas, W. P. (2012). What really works for English language learners:
Research-based practices for principals. In G. Theoharis & J. Brooks (Eds.), What every
principal needs to know to create equitable and excellent schools (pp. 155–173. Teachers
College Press.
Costa, A., Hernández, M., Costa-Faidella, J., & Sebastian-Galles, N. (2009). On the bilingual
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
13

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
advantage in conflict processing: Now you see it, now you don’t. Cognition, 113(2), 135-
149.
Devine, R. T. & Hughes, C. (2014). Relations between false belief understanding and executive
early childhood: a meta-analysis. Child Development, 85(5), 1777-1794.
Diaz, V., & Farrar, M. J. (2017). The missing explanation of the false-belief advantage in
bilingual children: A longitudinal study. Developmental Science, 21(4), e12594.
https://doi.org/10.1111/desc.12594
Dijkstra, T. (2005). Bilingual visual word recognition and lexical access. In J. F. Kroll & A.
M. B. de Groot (Eds.), Handbook of bilingualism: Psycholinguistic approaches (pp. 179-
201). Oxford University Press.
Dixson, D. D., Robberson, C. C. B., & Worrell, F. C. (2017) Psychosocial keys to African
American achievement? Examining the relationship between achievement and
psychosocial variable in high achieving African Americans. Journal of Advanced
Academics, 28(2), 120-140.
Duckworth, A. L., Peterson, C., Matthews, M. D., & Kelly, D. R. (2007). Grit:
Perseverance and passion for long-term goals. Journal of Personality and Social
Psychology, 92(6), 1087-1101. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.92.6.1087
Duncan, G., Dowsett, C., Classens, A., Magnuson, K., Huston, A., Klebanov, P., Pagani, L.,
Feinstein, L., Engel, Brooks-Gunn, J., Sexton, H., Duckworth, K., & Japel, C. (2007).
School readiness and later achievement. Developmental Psychology, 43, 1428-1446.
Dweck, C. S. (2000). Essays in social psychology. Self-theories: Their role in motivation,
personality, and development. Psychology Press.
Dweck, C. S. (2006). Mindset: The new psychology of success. Random House.
Dweck, C. S. (2007). The perils and promises of praise. Educational Leadership, 65(2), 34-39.
Dweck, C. S. (2008). Mindsets and math/science achievement. Prepared for the Carnegie
Corporation of New York-Institute for Advanced Study Commission on
Mathematics and Science Education.
Dweck, C., Chiu, C., & Hong, Y. (1995). Implicit theories and their role in judgments and
reactions: A world from two perspectives. Psychological Inquiry, 6(4), 267-285.
Dweck, C. S., & Leggett, E. L. (1988). A social-cognitive approach to motivation and
personality. Psychological Review, 95(2), 256–273.
Enriquez, G., Clark, S. R., & Della Calce, J. (2017). Using children’s literature for dynamic
frames and growth mindsets. Reading Teacher, 70(6), 711-719.
Farhadian, M., Abdullah, R., Mansor, M., Redzuan, M. Gazanizadand, N., & Kumar, V. (2010).
Theory of mind in bilingual and monolingual preschool children. American Journal of
Scientific Research, 7, 25-35.
Fraser, D. M. (2018). An exploration of the application and implementation of growth mindset
principles within a primary school. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 88, 645–
658.
Friesen, D. C., & Bialystok, E. (2012). Metalinguistic ability in bilingual children: The role of
executive control. Rivista di psicolinguistica applicata, 12(3), 47–56.
Frye, D., Zelazo, P. D., & Palfai, T. (1995). Theory of mind and rule-based reasoning. Cognitive
Development, 10(4), 483–527.
Genesee, F., Lindholm-Leary, K., Saunders, W., & Christian, D. (2006). Education English
language learners. Cambridge University Press.
Goetz, P. (2003). The effects of bilingualism on theory of mind development. Bilingualism:
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
14

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
Language and Cognition, 6(1), 1-15.
Goldhaber, D., & Özek, U. (2019). How much should we rely on student test achievement as a
measure of success? Educational Researcher, 48(7), 479-483.
Gort, M. & Sembiante, S. F. (2015). Navigating hybridized language learning spaces through
translanguaging pedagogy: Dual language preschool teachers’ languaging practices in
support of emergent bilingual children’s performance of academic discourse.
International Multilingual Research Journal, 9(1), 7–25.
Han, S., & Lee, K. (2013). Cognitive and affective perspective-taking ability of young
bilinguals in South Korea. Child Studies in Diverse Contexts, 3(1), 69–80.
Hanson, J., Bangert, A., & Ruff, W. G. (2016). Exploring the relationship between school growth
mindset and organizational learning variables: Implications for multicultural education.
Journal of Educational Issues, 2(2), 222-242.
Jones, K. & Mixon, J. R. (2016). Intercultural responsiveness in the second language learning
classroom. IGI Global.
Kaushanskaya, M., Gross, M., & Buac, M. (2014). Effects of classroom bilingualism on task
shifting, verbal memory, and word learning in children. Developmental Science, 17, 564–
583.
Kharkhurin, A. V. (2009). The role of bilingualism in creative performance on divergent
thinking and Invented Alien Creatures tests. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 43(1),
59–71. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2162-6057.2009.tb01306.x
Kharkhurin, A. V. (2010). Sociocultural differences in the relationship between bilingualism and
creative potential. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 41(5-6), 776–
783. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022022110361777
Knapp, P., & Beck, A. T. (2008). Cognitive therapy: Foundations, conceptual models,
applications and research. Revista Brasileira de Psiquiatria, 30(Suppl2), S54
S64. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-44462008000600002
Kovács, A. M. (2009). Early bilingualism enhances mechanisms of false-belief reasoning.
Developmental Sciences, 12, 48-54. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7687.2008.00742.x
Kroll, J. F., Dussias, P. E., Bogulski, C. A., & Valdes-Kroff, J. (2012). Juggling two languages in
one mind: What bilinguals tell us about language processing and its consequences for
cognition. The Psychology of Learning and Motivation, 56, 229-262.
Kroll, J. F. & Dussias, P. E. (2013). The comprehension of words and sentences in two
languages. In T. Bhatia & W. Ritchie (Eds.), The handbook of bilingualism and
multilingualism (2nd ed., pp. 216–243). Wiley-Blackwell Publishers.
Leikin, M., & Tovli, E. (2014). Bilingualism and creativity in early childhood. Creativity
Research Journal, 26(4), 411-417.
Lindholm-Leary, K. J. (2005). The rich promise of two-way immersion. Educational Leadership,
62(4), 56-59.
Lindholm-Leary, K., & Borsato, G. (2006). Academic achievement. In F. Genesee, K. Lindholm
Leary, W. Sanders, & D. Christian (Eds.), Educating English language learners: A
synthesis of research evidence (pp. 176-222). Cambridge University Press.
Lindsey, R. B., Nuri Robins, K., & Terrell, R. D. (2009). Cultural proficiency: A manual for
school leaders (3rd ed.). Corwin.
Lippard, C. N., Lamm, M. H., Tank, K. M., & Young Choi, J. (2018). Pre-engineering thinking
and the engineering habits of mind in preschool classroom. Early Childhood Education
Journal, 47(187), 187-198.
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
15

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
Mangels, J. A., Butterfield, B., Lamb, J., Good, C., & Dweck, C. S. (2006). Why do beliefs about
intelligence influence learning success? A social cognitive neuroscience model. Social
Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 1(2), 75–86.
Marulis, L. M. & Neuman, S. (2013). How vocabulary interventions affect young children at
risk: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness, 6(3),
223-262.
McFarland, J., Cui, J., Rathbun, A., & Holmes, J. (2018). Trends in high school dropout and
completion rates in the United States: 2018 (NCES 2019-117). U.S. Department of
Education, National Center for Education Statistics.
Mendez, J. L., & Westerberg, D. (2012). Implementation of a culturally adapted treatment to
reduce barriers for Latino parents. Cultural Diversity and Ethnic Minority Psychology,
18(4), 363-372.
Moser, J. S., Schroder, H. S., Heeter, C., Moran, T. P., & Lee, Y. H. (2011). Mind your errors:
Evidence for a neural mechanism linking growth mind set to adaptive post-error
adjustments. Psychological Science, 22, 1484-1489.
Meisel, J. (2004). The bilingual child. In T. Bhatia & W. Ritchie (Eds.), The handbook of
bilingualism (pp. 91-113). Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Mindset Works Inc. (2017). The impact of a growth mindset. Retrieved from
https://www.mindsetworks.com/Science/Impact
Mindset Works Inc. (2017). Grow their mindsets from the beginning with GEM. Retrieved from
https://www.mindsetworks.com/programs/gem
Moser, J. S., Schroder, H. S., Heeter, C., Moran, T. P., & Lee, Y. H. (2011). Mind your errors:
Evidence for a neural mechanism linking growth mind set to adaptive post-error
adjustments. Psychological Science, 22, 1484-1489.
Nussbaum, A. D., & Dweck, C. S. (2007). Defensiveness vs. remediation: Self-theories and
modes of self-esteem maintenance. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 34(5),
599-612.
Orosz, G., Péter-Szarka, S., Bőthe, B., Tóth-Király, I., & Berger, R. (2017). How not to do a
mindset intervention: Learning from a mindset intervention among students with good
grades. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, Article 311.
O’Rourke, E., Haimovitz, K., Ballweber, C., Dweck, C., & Popovic, Z. (2014). Brain points: A
growth mindset incentive structure boosts persistence in an educational game. In
Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp.
3339-3348). ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/2556288.2557157
Ortiz, A. A., & Fráquiz, M. E. (2017). Co-editors’ introduction: Early childhood education
programs for dual language learners: Opportunities and challenges. Bilingual Research
Journal, 42(3), 269-274.
Park, M., O’Toole, A., & Katsiaficas, C. (2017). Dual language learners: A demographic and
policy profile for California. Migration Policy Institute.
Park, M., Zong, Jie, & Batalova, J. (2018). Growing superdiversity among young U.S. dual
language learners and its implications. Migration Policy Institute.
Paradis, J., Genesee, F., & Crago, M. (2011). Dual language development and disorders: A
handbook on bilingualism & second language learning. Paul H. Brookes Publishing.
Pawlina, S. & Stanford, C. (2011). Preschools grow their brains: Shifting mindsets for greater
resiliency and better problem solving. Young Children, 66(5), 30-35.
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
16

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
Peal, E., & Lambert, W. E. (1962). The relation of bilingualism to intelligence. Psychological
Monographs, 76, 1-23.
Pearson, B. Z., Fernandez, S. C., Lewedeg, V., & Oller, D. K. (1997). The relation of input
factors to lexical learning by bilingual infants. Applied Psycholinguistics, 18, 41-58.
Premack, D., & Woodruff, G. (1978). Does the chimpanzee have a theory of mind? Behavioral
and Brain Sciences, 1(4), 515–526.
Rattan, A., Savani, K., Komarraju, M., Morrison, M. M., Boggs, C., & Ambady, N. (2018).
Meta-lay theories of scientific potential drive underrepresented students’ sense of
belonging to science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). Journal of
Personality and Social Psychology, 115(1), 54–75.
Ravenscroft, S. P., Waymire, T. R., & West, T. D. (2012). Accounting students’ metacognition:
The association of performance, calibration error, and mindset. Issues in Accounting
Education, 27(3), 707-732.
Reavis, R., Miller, S., Grimes, J., & Fomukong, A. (2018). Effort as person-focused
praise: “Hard worker” has negative effects for adults after a failure. Journal of Genetic
Psychology, 179(3), 117-122.
Sabbagh, M. A., Xu, F., Carlson, S. M., Moses, L. J., & Lee, K. (2006). The development of
executive functioning and theory of mind. Psychological Science, 17(1), 74-81.
Scheffner Hammer, C., Hoff, E., Uchikoshi, Y., Gillanders, C., Castro, D. C., & Sandilos, L. E.
(2014). The language and literacy development of young dual language learners: A
critical review. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 29(4), 715-733.
Schmidt, J. A., Shumow, L., & Kackar-Cam, H. Z. (2017). Does mindset intervention predict
students’ daily experience in classrooms? A comparison of seventh and ninth graders’
trajectories. Journal of Youth Adolescence, 46(3), 582-602.
Schroeder, S. R. (2018). Do bilinguals have an advantage in theory of mind? A meta-analysis.
Frontiers in Communication, 3(36), 1-8. https://doi.org/ 10.3389/fcomm.2018.00036.
Schroeder, S. R., & Marian, V. (2012). A bilingual advantage for episodic memory in older
adults. Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 24(5), 591-601.
Schroder, H. S., Fisher, M. E., Lin, Y., Lo, S. L., Danovitch, J. H., & Moser, J. S. (2017). Neural
evidence for enhanced attention to mistakes among school-aged children with a growth
mindset. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 24, 42–50.
Smiley, P. A., & Dweck, C. S. (1994). Individual differences in achievement goals among young
children. Child Development, 65(6), 1723– 1743.
Soveri, A., Laine, M., Hämäläinen, H., & Hugdahl, K. (2011). Bilingual advantage in
attentional control: Evidence from the forced-attention dichotic listening paradigm.
Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 14(03), 371–378.
Sugarman, J., & Geary, C. (2018). English learners in select states: Demographics, outcomes,
and state accountability policies. Migration Policy Institute.
Thierry, G., & Wu, Y.J. (2007). Brain potential reveal unconscious translation during language
comprehension. PNAS, 104(30), 12530-12535.
U.S. Department of Education (2015). Dual language education programs: Current state
policies and practices. Office of English Language Acquisition.
Valentino, R. A., & Reardon, S. F. (2015). Effectiveness of four instructional programs designed
to serve English learners: Variation by ethnicity and initial English proficiency.
Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 37(4), 612-637.
Wang, C., Luo, J., Nie, P., & Wang, D. (2019). Growth mindset can reduce the adverse effect of
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
17

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
substance use on adolescent reasoning. Frontiers in Psychology, 10(1852), 1-8.
Wellman, H. M., Cross, D. R., & Watson, J. (2001). Meta-analysis of theory-of-mind
development: The truth about false belief. Child Development, 72(3), 655-684.
Williams, C. P. (2014). Chaos for dual language learners: An examination of state policies for
exiting children from language services in the preK-3rd grade. New American
Foundation.
Wiseheart, M., Viswanathan, M., & Bialystok, E. (2016). Flexibility in task switching by
monolinguals and bilinguals. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 19(1), 141-146.
Yeager, D. S., Hanselman, P., Walton, G. M., Murray, J. S., Crosnoe, R., Muller, C., Tipton, E.,
Schneider, B., Hulleman, C. S., Hinojosa, C. P., Paunesku, D., Romero, C., Flint, K.,
Roberts, A., Trott, J., Iachan, R., Buontempo, J., Yang, S. M., Carvalho, C. M., Hahn, P.
R., Gopalan, M., Mhatre, P., Ferguson, R., Duckworth, A. L., & Dweck, C. S. (2019). A
national experiment reveals where a growth mindset improves academic achievement.
Nature, 573(7774), 364-369.
Yettick, H., Lloyd, S., Harwin, A., Riemer, A., & Swanson, C. B. (2016). Mindset in the
classroom: A national study of K-12 teachers. Editorial Projects in Education.
https://www.edweek.org/ew/projects/mindset-in-the-classroom-a-national-study.html
Yoshida, H. (2008). The cognitive consequences of early multilingualism. ZERO TO THREE
Journal, 2, 26–30.
Zhou, B. & Krott, A. (2016). Data trimming procedure can eliminate bilingual cognitive
advantage. Psychonomic Society, Inc., 23, 1221-1230.
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
18

Grote et al: Bilingual Cognition and Growth Mindset
Author Notes
Kandice S. Grote, Ph.D.
Assistant Professor, Child and Adolescent Development
California State University Northridge
kandice.grote@csun.edu
Emily E. Russell, Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Child and Adolescent Development
California State University Northridge
emily.russell@csun.edu
Olivia Bates, B.S.
olivia.bates.347@my.csun.edu
Rosemary Gonzalez, Ph.D.
Professor, Child and Adolescent Development & Chicana/o Studies
rosemary.gonzalez@csun.edu
More details of this Creative Commons license are available at
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/. Current Issues in
Education is published by the Mary Lou Fulton Institute and Graduate
School of Education at Arizona State University.
Current Issues in Education, 22(2)
19
